Again another awesome lesson from my buddy Lexx 😄
here’s how I suggest combining the listed libraries effectively:
1. Parsing Inputs
Preprocessing Text:
compromise – Tokenize and parse sentences, extract structured data (names, dates, etc.).
Natural – Additional NLP utilities like stemming, tokenizing, and classification.
ml5.js – For more advanced NLP tasks like sentiment analysis and named-entity recognition.
2. Understanding Context and Intent
Intent and Tone Detection:
sentiment – Analyze sentiment to tag the tone (positive, negative, neutral).
ml5.js – For model-based intent classification or sentiment detection.
3. Structuring Data
Convert parsed input into structured JSON objects, storing:
Words and Pairs for context.
Intent and Tone metadata.
4. Storing and Retrieving Data
Flatfile Database:
fs (Node.js) – Simple JSON-based storage for small-scale data.
SQLite Alternative:
sqlite3 – For relational storage of structured input data if needed.
5. Transforming Data
Transformers:
tensorflow/tfjs – Leverage machine learning models to generate contextual replies or transform input data.
brain.js – For basic neural network implementations if tfjs is overkill.
Suggested Flowchart
User Input
➔ Preprocessing (with compromise and Natural).
➔ Sentiment & Intent Detection (with sentiment and ml5.js).
➔ Create Structured JSON (words, pairs, intent, tone).
➔ Store in Flatfile/SQLite (with fs or sqlite3).
➔ Generate Response (with tfjs or brain.js).
added SearchEngine.js to scripts utilising
- elasticlunr GitHub Link-
With this falling under MIT licence its perfect
Example from Lexx:
const elasticlunr = require('elasticlunr');
// Initialize the search index
const index = elasticlunr(function () {
this.addField('content');
this.setRef('id');
});
// Function to add documents to the index
function addDocument(id, content) {
index.addDoc({ id, content });
}
// Function to search the index
function search(query) {
return index.search(query, { expand: true });
}
module.exports = { addDocument, search };
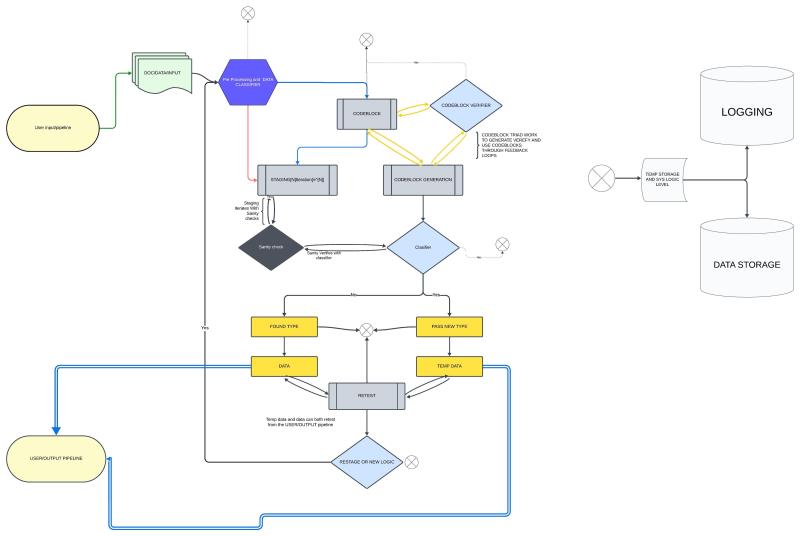
Adaptive Pipeline the self organising database concept
🛠️ Overview of the Adaptive Pipeline
Initial Parsing & Analysis:
Break down input using NLP tools (e.g., Compromise, Natural, ml5.js).
Identify words, pairs, parts of speech, and semantic context.
Dynamic Pipeline Generation:
If a new type of pattern is identified, generate a new processing pipeline tailored for that data.
Similar data automatically flows through the existing or new pipeline.
Self-Organizing Database:
Store parsed data and relationships.
Optimize the structure based on how frequently different patterns are accessed or learned.
Continuous Learning & Adaptation:
As the system encounters new data, it updates pipelines and restructures data storage to improve efficiency.
Reinforce weights and relationships dynamically.
⚙️ Step-by-Step Implementation
1. Parsing and Analysis Stage
Leverage NLP tools for breaking down input:
Compromise and Natural for tokenization, POS tagging, and basic NLP tasks.
ml5.js for higher-level ML-based tasks like sentiment analysis or entity recognition.
Example Parsing Function:
const nlp = require('compromise');
const { SentimentAnalyzer, PorterStemmer } = require('natural');
function parseInput(sentence) {
// Tokenize and analyze sentence
const doc = nlp(sentence);
const tokens = doc.terms().out('array');
const sentiment = new SentimentAnalyzer('English', PorterStemmer).getSentiment(tokens);
return {
root: sentence,
words: tokens,
sentiment: sentiment >= 0 ? 'positive' : 'negative'
};
}
console.log(parseInput("I went to the restroom."));
2. Dynamic Pipeline Creation
If a new pattern emerges, create a specialized pipeline to handle similar inputs efficiently.
Example Logic for Pipeline Creation:
const pipelines = {};
function processWithDynamicPipeline(data) {
const patternKey = identifyPattern(data); // Function to determine data type/pattern
if (!pipelines[patternKey]) {
pipelines[patternKey] = createNewPipeline(patternKey); // Create a new pipeline dynamically
}
return pipelines[patternKey](data); // Process data through the appropriate pipeline
}
// Placeholder for pattern identification
function identifyPattern(data) {
return data.sentiment; // For example, categorize by sentiment
}
// Placeholder for creating a new pipeline
function createNewPipeline(pattern) {
return (data) => {
console.log(`Processing data through the ${pattern} pipeline.`);
return data;
};
}
const result = processWithDynamicPipeline(parseInput("This is amazing!"));
console.log(result);
3. Self-Organizing Storage System
Store the parsed results and dynamically link relationships based on semantic weights and patterns.
Example Database Structure:
{
"patterns": {
"positive": {
"examples": [
{ "sentence": "This is amazing!", "words": ["This", "is", "amazing"] }
],
"links": ["happy", "excited"]
},
"negative": {
"examples": [
{ "sentence": "This is terrible!", "words": ["This", "is", "terrible"] }
],
"links": ["sad", "disappointed"]
}
}
}
4. Continuous Learning and Optimization
When new data is encountered:
Check if it matches an existing pattern.
If not, create a new pipeline and store relationships.
Optimize the database by merging similar patterns and updating weights.
Example of Learning Logic:
function learnNewData(data) {
const pattern = identifyPattern(data);
if (!pipelines[pattern]) {
pipelines[pattern] = createNewPipeline(pattern);
}
storeInDatabase(data, pattern);
}
function storeInDatabase(data, pattern) {
if (!database.patterns[pattern]) {
database.patterns[pattern] = { examples: [], links: [] };
}
database.patterns[pattern].examples.push(data);
}
// Sample execution
learnNewData(parseInput("This was an incredible experience!"));
console.log(database);
🌱
How It All Comes Together
🔄 Flowchart of the System
Input ➔ Parsing (Compromise/Natural/ml5.js)
Pattern Identification ➔ Pipeline Selection/Creation
Dynamic Processing ➔ Self-Organizing Storage
Continuous Learning ➔ Optimization of Pipelines and Database
🚀 Benefits
Scalability: Automatically grows and adapts to new patterns.
Efficiency: Optimized pipelines mean faster processing over time.
Flexibility: Easily accommodates new types of data and relationships.
Intelligence: Learns dynamically, building a smarter, more context-aware system.
Start for database structure and internal data object contents:
V1
{
"root": "This could lead to a self-evolving, context-aware database — something truly new and adaptable.",
"words": [
{ "word": "lead", "POS": "Verb", "weight": 0.9, "context": ["guide", "result in"], "sentiment": "neutral" },
{ "word": "self-evolving", "POS": "Adjective", "context": ["adaptive", "self-improving"], "synonyms": ["autonomous"], "weight": 0.85 }
],
"pairs": [
{ "pair": "could lead", "relation": {"type": "cause-effect", "context": "future potential outcome"}, "weight": 0.8 }
],
"intent": "educate",
"tone": "friendly",
"sentiment": "neutral"
}
V2
{
"root": "Can you help me find the nearest coffee shop?",
"words": [
{ "word": "Can", "POS": "Modal", "weight": 0.8 },
{ "word": "help", "POS": "Verb", "weight": 0.9 },
{ "word": "find", "POS": "Verb", "weight": 0.85 },
{ "word": "coffee", "POS": "Noun", "weight": 0.9, "context": ["drink", "beverage"] },
{ "word": "shop", "POS": "Noun", "weight": 0.85, "context": ["store", "location"] }
],
"pairs": [
{ "pair": "help find", "relation": {"type": "action", "context": "assistance"}, "weight": 0.9 },
{ "pair": "coffee shop", "relation": {"type": "destination", "context": "place"}, "weight": 0.95 }
],
"intent": "request",
"tone": "polite",
"sentiment": "neutral",
"metadata": {
"source": "user_input",
"timestamp": "2024-06-11T10:30:00Z",
"confidence": {
"intent": 0.92,
"sentiment": 0.88,
"POS": 0.95
},
"processed_by": ["compromise", "ml5.js", "Natural"]
}
}
Building a AIO(all in one) input system Premise and logic Behind AI response
Possible flow logic for storage and integrated mechanical stages
4